Infection by parasites can sometimes provide health benefits. One example is the interplay between infection with helminths and reduction in the symptoms of allergic diseases such as asthma. Helminths secrete a cocktail of immune effectors which suppress different parts of our immune systems, thereby aiding their survival. However, some of these effectors prove beneficial to the host, reducing inflammatory illness. How do they function and what can we learn from helminths about how to develop highly selective immuno-modulators?
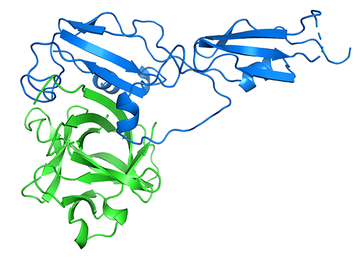
HpARI is formed from three modules, known as CCP domains. Abhishek’s structure showed how two of these, CCP2 and CCP3 bind to IL-33. Most of the interaction was mediated by CCP2, which forms an extensive interface with IL-33. However, CCP2 does not stop IL-33 from binding to its receptor ST2. Indeed, CCP2 alone may stabilise the active form of IL-33, perhaps allowing it to function for longer and throughout more of the body. In contrast, the interaction between CCP3 of HpARI and IL-33 is mediated by a long loop which protrudes from CCP3 and directly blocks IL-33 from binding to ST2.
Abhishek was able to test this finding, showing that HpARI variants lacking CCP3 or its long loop, could not prevent formation of the IL-33:ST2 signalling complex. This was followed up by Florent Colomb and Henry, who showed that these truncated HpARI variants are also unable to block signalling by IL-33 in a cell-based assay or to prevent immune responses in a model of asthma.
This study shows, for the first time, how a helminth blocks the function of an important host cytokine. We also provide the first view of IL-33 bound to any of its inhibitors. The next step will be to learn from the helminth how to make effective therapeutics which prevent IL-33 mediated signalling. Perhaps the designers of the next generation of anti-asthma medications will learn from a parasite!
Jamwal, A., Colomb, F., McSorley, H.J.* and Higgins, M.K.* (2023) Structural basis for IL-33 recognition and its antagonism by the helminth effector protein HpARI. Nature Communications 15 5226